Normalization¶
StreamAlert has an unannounced feature Data Normalization. In its current implementation, it extracts recognized field names from classified records, and saves them to a top-level key on the same record.
This is useful for rules, as they can be written to compare data fields against IoCs, such as IP Address, instead of writing one rule for each incoming data type. However, there are couple limitations we have identified as we use Normalization internally for a while.
Normalization 2.0 (Reboot)¶
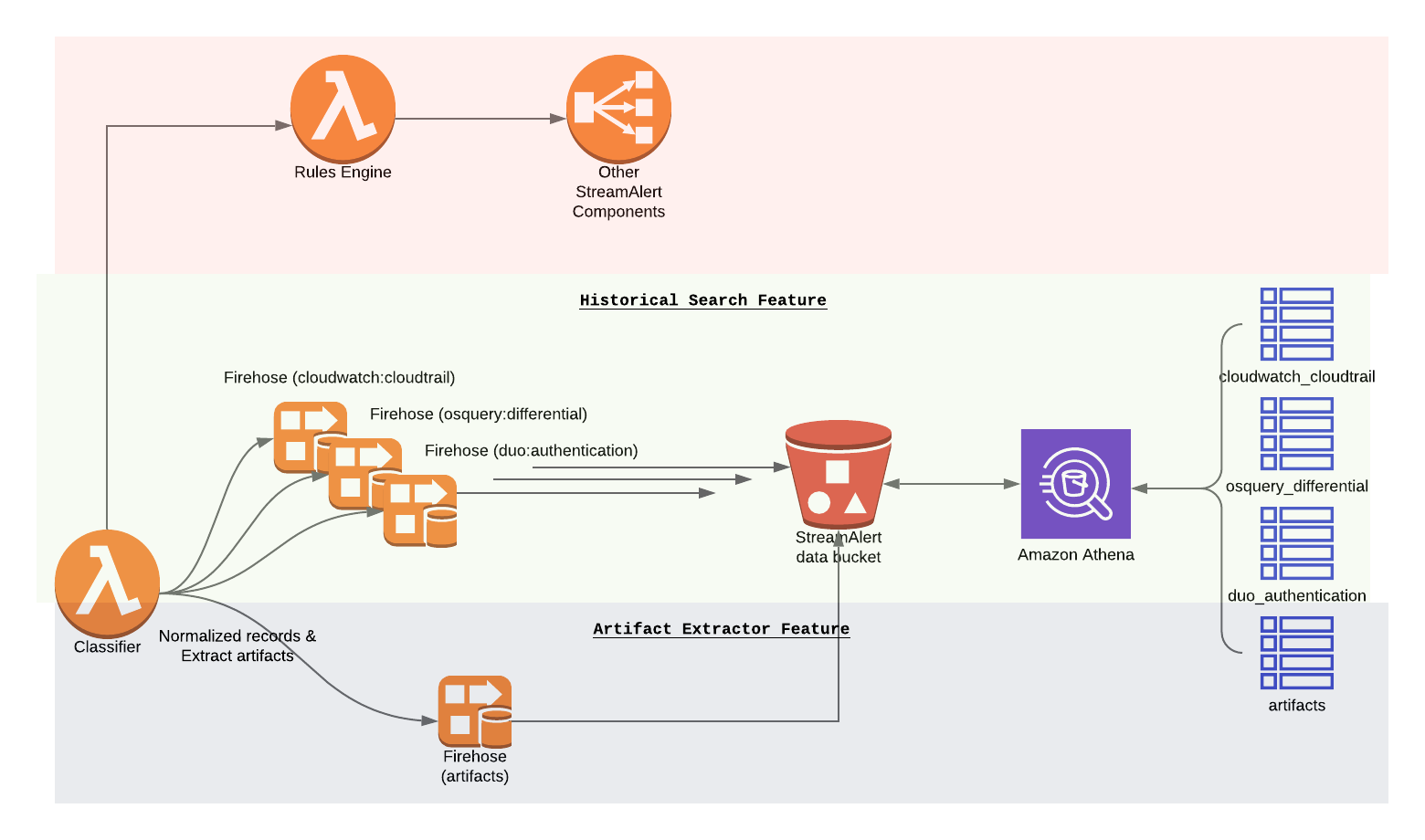
In Normalization 2.0, we introduce a new lambda function Artifact Extractor by leveraging Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose Data Transformation feature to extract interesting artifacts from records processed by classifiers. The artifacts will be stored in the same S3 bucket where StreamAlert Historical Search feature uses and the Artifacts will be available for searching via Athena as well.
Artifacts Inventory¶
An artifact is any field or subset of data within a record that bears meaning beyond the record itself, and is of interest in computer security. For example, a “carbonblack_version” would not be an artifact, as it is meaningless outside of the context of Carbon Black data. However, an ip_address would be an artifact.
Artifact Extractor Lambda function will build an artifacts inventory based on S3 and Athena services. It enables users to search for all artifacts across whole infrastructure from a single Athena table.
Configuration¶
In Normalization v1, the normalized types are based on log source (e.g. osquery, cloudwatch, etc) and defined in conf/normalized_types.json file.
In Normalization v2, the normalized types will be based on log type (e.g. osquery:differential, cloudwatch:cloudtrail, cloudwatch:events, etc) and defined in conf/schemas/*.json. Please note, conf/normalized_types.json will is deprecated.
All normalized types are arbitrary, but only lower case alphabetic characters and underscores should be used for names in order to be compatible with Athena.
Supported normalization configure syntax:
"cloudwatch:events": { "schema": { "field1": "string", "field2": "string", "field3": "string" }, "parser": "json", "configuration": { "normalization": { "normalized_key_name1": [ { "path": ["path", "to", "original", "key"], "function": "The purpose of normalized_key_name1", "condition": { "path": ["path", "to", "other", "key"], "is|is_not|in|not_in|contains|not_contains": "string or a list" }, "send_to_artifacts": true|false } ] } } }
normalized_key_name1: An arbitrary string to name the normalized key, e.g.ip_address,hostname,commandetc.path: A list contains a json path to the original key which will be normalized.function: Describe the purpose of the normalizer.condition: An optional block that is executed first. If the condition is not met, then this normalizer is skipped.path: A list contains a json path to the condition key.is|is_not|in|not_in|contains|not_contains: Exactly one of these fields must be provided. This is the value that the conditional field that is compared against. E.g"condition": { "path": ["account"], "is": "123456" } "condition": { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "userName"], "in": ["root", "test_username"] }
Note
Use all lowercases string a list of strings in the conditional field. The value from the record will be converted to all lowercases.
send_to_artifacts: A boolean flag indicates should normalized information sent toartifactstable. This field is optional and it is default totrue. It thinks all normalized information are artifacts unless set this flag tofalseexplicitly.
Below are some example configurations for normalization v2.
Normalize all ip addresses (
ip_address) and user identities (user_identity) forcloudwatch:eventslogsconf/schemas/cloudwatch.json"cloudwatch:events": { "schema": { "account": "string", "detail": {}, "detail-type": "string", "id": "string", "region": "string", "resources": [], "source": "string", "time": "string", "version": "string" }, "parser": "json", "configuration": { "normalization": { "ip_address": [ { "path": [ "detail", "sourceIPAddress" ], "function": "Source IP addresses" } ], "user_identity": [ { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "type"], "function": "User identity type", "send_to_artifacts": false }, { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "arn"], "function": "User identity arn" }, { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "userName"], "function": "User identity username" } ] } } }
Normalize all commands (
command) and file paths (file_path) forosquery:differentiallogsconf/schemas/osquery.json"osquery:differential": { "schema": { "action": "string", "calendarTime": "string", "columns": {}, "counter": "integer", "decorations": {}, "epoch": "integer", "hostIdentifier": "string", "log_type": "string", "name": "string", "unixTime": "integer", "logNumericsAsNumbers": "string", "numerics": "string" }, "parser": "json", "configuration": { "optional_top_level_keys": [ "counter", "decorations", "epoch", "log_type", "logNumericsAsNumbers", "numerics" ], "normalization": { "command": [ { "path": ["columns", "command"], "function": "Command line from shell history" } ], "file_path": [ { "path": ["columns", "history_file"], "function": "Shell history file path" } ] } } }
Normalize username (
user_identity) forcloudwatch:eventslogs when certain condition is met. In the following example, it will only normalize username related to AWS accounts11111111and22222222.conf/schemas/cloudwatch.json"cloudwatch:events": { "schema": { "account": "string", "detail": {}, "detail-type": "string", "id": "string", "region": "string", "resources": [], "source": "string", "time": "string", "version": "string" }, "parser": "json", "configuration": { "normalization": { "user_identity": [ { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "userName"], "function": "User identity username", "condition": { "path": ["account"], "in": ["11111111", "22222222"] } } ] } } }
Deployment¶
Artifact Extractor will only work if Firehose and Historical Search are enabled in
conf/global.json"infrastructure": { ... "firehose": { "use_prefix": true, "buffer_interval": 60, "buffer_size": 128, "enabled": true, "enabled_logs": { "cloudwatch": {}, "osquery": {} } } ... }
Enable Artifact Extractor feature in
conf/global.json"infrastructure": { "artifact_extractor": { "enabled": true, "firehose_buffer_size": 128, "firehose_buffer_interval": 900 }, "firehose": { "use_prefix": true, "buffer_interval": 60, "buffer_size": 128, "enabled": true, "enabled_logs": { "cloudwatch": {}, "osquery": {} } } ... }
Artifact Extractor feature will add few more resources by running
buildCLIIt will add following resources.
A new Glue catalog table
artifactsfor Historical Search via AthenaA new Firehose to deliver artifacts to S3 bucket
New permissions
python manage.py build --target artifact_extractor
Then we can deploy
classifierto enable Artifact Extractor feature.python manage.py deploy --function classifier
Note
If the normalization configuration has changed in
conf/schemas/*.json, make sure to deploy the classifier Lambda function to take effect.
Custom Metrics¶
Add additional three custom metrics to Classifier for artifacts statistics.
ExtractedArtifacts: Log the number of artifacts extracted from the recordsFirehoseFailedArtifats: Log the number of records (artifacts) failed sent to FirehoseFirehoseArtifactsSent: Log the number of records (artifacts) sent to Firehose
By default, the custom metrics should be enabled in the Classifier, for example in conf/clusters/prod.json
{ "id": "prod", "classifier_config": { "enable_custom_metrics": true, ... } }python manage.py build --target "metric_filters_*"
Artifacts¶
Artifacts will be searchable within the Athena
artifactstable while original logs are still searchable within dedicated table.
Search
cloudwatch:eventslogs:SELECT * FROM PREFIX_streamalert.cloudwatch_events WHERE dt='2020-06-22-23'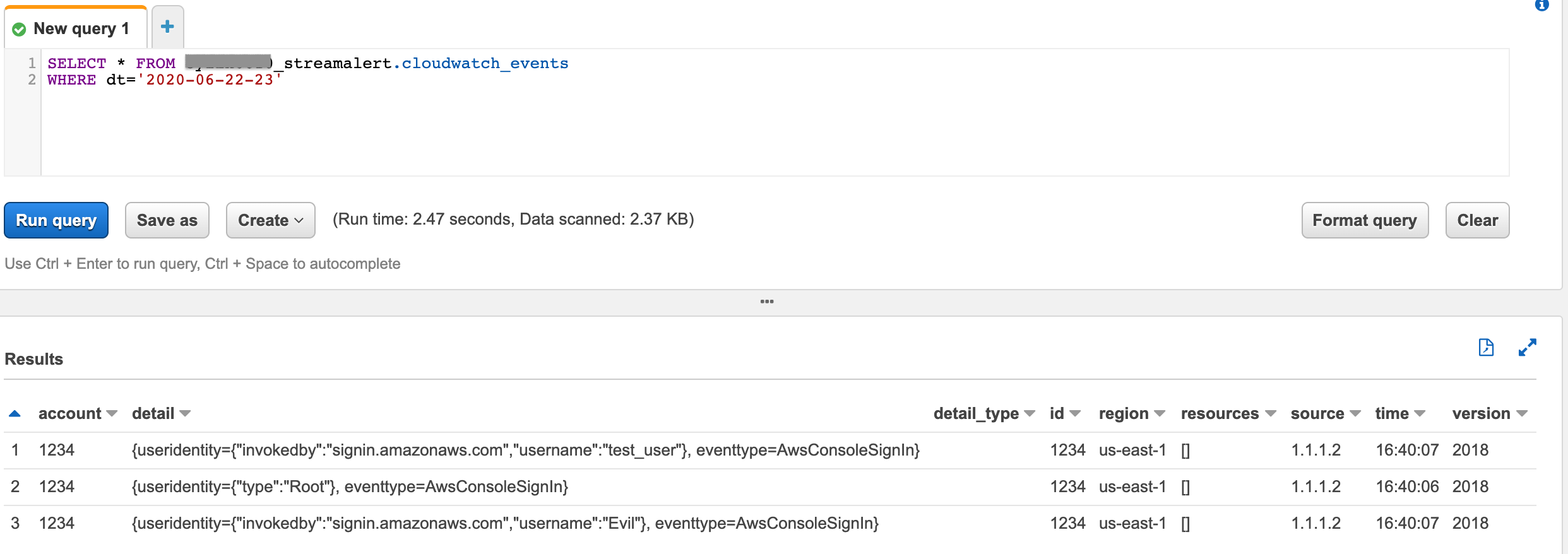
(click to enlarge)¶
All artifacts, including artifacts extracted from
cloudwatch:events, will live inartifactstable.
SELECT * FROM PREFIX_streamalert.artifacts WHERE dt='2020-06-22-23'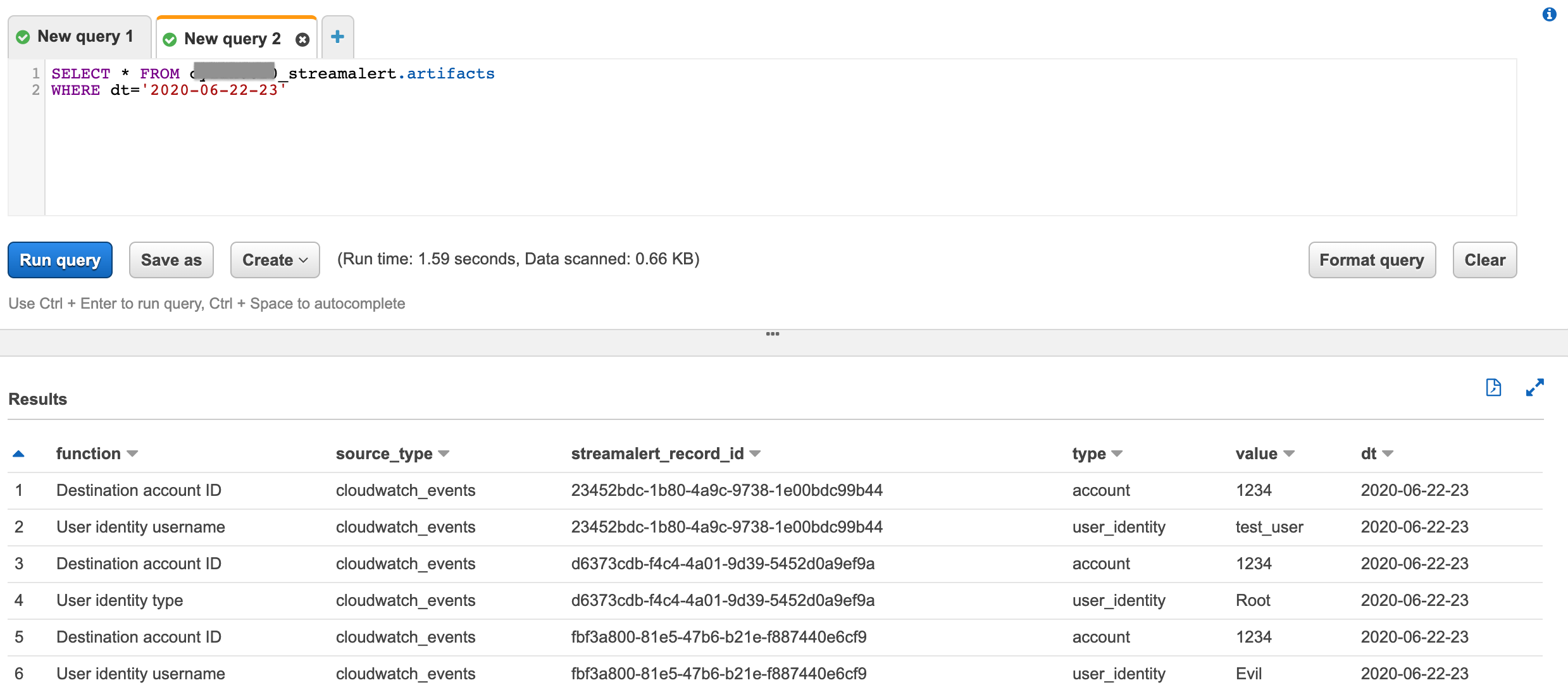
(click to enlarge)¶
(Advanced) Use join search to find original record associated to the artifacts by
streamalert_record_id
SELECT artifacts.*, cloudwatch.* FROM (SELECT streamalert_record_id AS record_id, type, value FROM PREFIX_streamalert.artifacts WHERE dt ='2020-06-22-23' AND type='user_identity' AND LOWER(value)='root' LIMIT 10) AS artifacts LEFT JOIN (SELECT streamalert_normalization['streamalert_record_id'] AS record_id, detail FROM PREFIX_streamalert.cloudwatch_events WHERE dt ='2020-06-22-23' LIMIT 10) AS cloudwatch ON artifacts.record_id = cloudwatch.record_id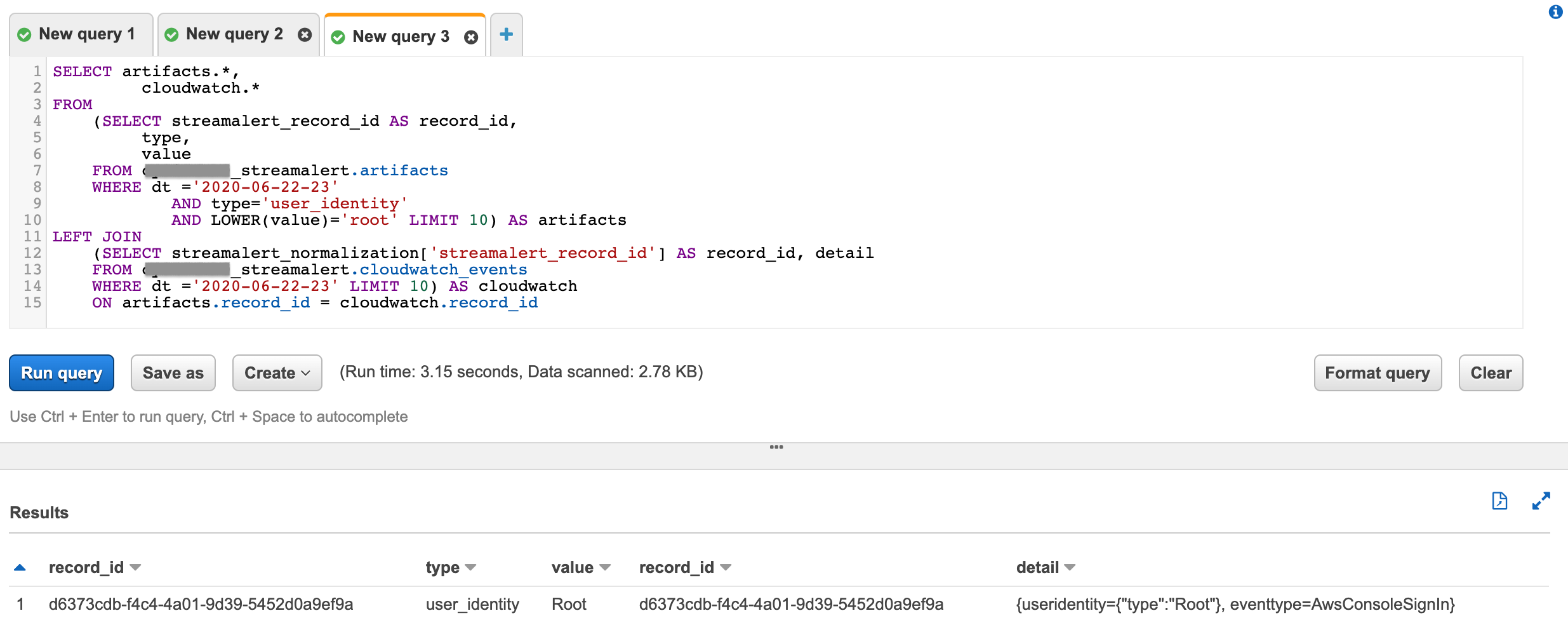
(click to enlarge)¶
Note
Instead issue two searches, we can use JOIN statement to search once across two tables to find the original record(s) associated with the interesting artifacts. This requires
streamalert_normalizationfield where containsstreamalert_record_idsearchable in the original table. Current process is addstreamalert_normalizationfield as a top level optional key to the schema.
Update schema
conf/schemas/cloudwatch.json"cloudwatch:events": { "schema": { "account": "string", "detail": {}, "detail-type": "string", "id": "string", "region": "string", "resources": [], "source": "string", "streamalert_normalization": {}, "time": "string", "version": "string" }, "parser": "json", "configuration": { "optional_top_level_keys": [ "streamalert_normalization" ], "normalization": { "user_identity": [ { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "type"], "function": "User identity type" }, { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "arn"], "function": "User identity arn" }, { "path": ["detail", "userIdentity", "userName"], "function": "User identity username" } ] } } }Apply the change by running
python manage.py build --target "kinesis_firehose_*"
Considerations¶
The Normalization Reboot will bring us good value in terms of how easy will be to search for artifacts across entire infrastructure in the organization. It will also make it possible to write more efficient scheduled queries to have correlated alerting in place. But, it is worth to mention that there may have some tradeoffs on requiring additional resources, adding additional data delay.
Increase in Data Footprint: Each individual original record has the chance to add many artifacts. In practice, this will likely not be a huge issue as each artifact is very small and only contains few fields.
Additional Delay: Firehose data transformation will add additional up to 900 seconds of delay on the data available for historical search. 900 seconds is a configurable setting on the Firehose where the artifacts extracted from. Reduce the firehose buffer_interval value if want to reduce delay.
High memory usage: Artifact Extractor Lambda function may need at least 3x max(buffer size of firehoses where the artifacts extracted from). Because we are doing lots of data copy in Artifact Extractor lambda function. This may be improved by writing more efficient code in the Artifact Extractor Lambda function..